Outlines current management of upper limb conditions in primary care settings
This information is for primary care physicians and a general summary of current practice
Please consult a physician directly for management of specific injuries
2nd - 5th Metacarpal Fractures: Indications for Operative Management
Mechanism of Injury: Fall onto outstretched hand, direct impact to metacarpals (crush injury) or direct blow to metacarpal heads (i.e punch injury)
Consideration: 4th and 5th MC's are more mobile and therefore more unstable compared to 2nd and 3rd MC's
Associated injuries: Extensor tendon injury
Rotation of Metacarpal Fractures
-
No rotation tolerated as it impacts functional use of the fingers (i.e gripping, fine motor and pinch)
-
Difficult to assess on x-ray
-
Assess by having patient make a fist (if tolerable for patient)
Intra-articular Metacarpal Head Fractures
-
Some MC neck fractures impact the MCP joint and require fixation
-
Can be misdiagnosed as a boxers fracture (5th MC neck fracture)
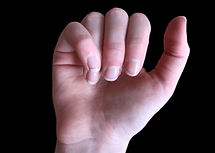
Rotation of the 5th metacarpal fracture leading to scissoring of the little finger
Compound Metacarpal Fracture
-
Skin breached
-
Exposed fracture
-
Open wound
Multiple Metacarpal Fractures
-
Stability of metacarpals is reinforced by adjacent metacarpals and soft tissues
-
Multiple metacarpal fractures reduce stability and increase the risk of fracture migration

Multiple Metacarpal Fractures
Dorsal Angulation of Metacarpal Fractures
-
4th and 5th metacarpals are quite mobile compared to 2nd and 3rd metacarpals and can tolerate a higher degree of dorsal angulation with minimal functional impact to patients
-
See table
Shortening of Metacarpal Fractures
-
Up to 6mm shortening tolerated at all metacarpals
-
Can lead to loss of metacarpal head prominence in a fist
-
consideration for patients who participate in boxing or fighting sports
-
-
Potential risks include an extensor lag of the MCPJ

ULQ specialists are available to see patients and assess the above.
If patients require non-operative management, we are able to directly refer them to hand therapy for protective splinting.

